Problem Solving Techniques LEAN
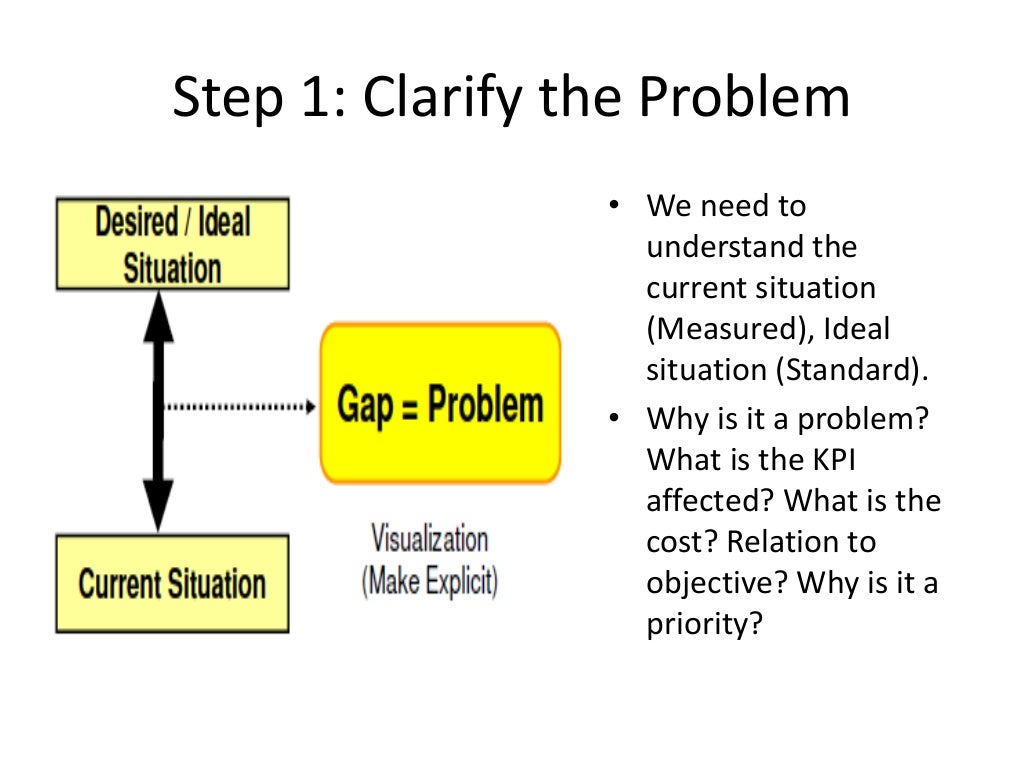
The lean problem-solving process is a cycle of observation, assessment, and continual evaluation. As shown in Table 6.1, this cycle typically involves eight specific steps. Steps in the Toyota Lean Problem-Solving Process. Step Action; Step 1: Clarify the problem. Step 2:
Lean Six Sigma Problem Solving Process Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Riset
The process outlined four basic steps of problem solving in the TWI framework to help train people, improve work methods and resolve problems in a structured way: In the 1960's, various 6-step approaches were created. These can be summarised as follows: Six Step Method: In the 1960's and 70's the concept of "kaizen" emerged in Japan.
Clarifying the '5 Whys' ProblemSolving Method Lean Enterprise Institute
Lean Problem Solving is a way of approaching organizational problems that is characterized by continuous improvement and the use of proven, problem-solving methodologies. The goals of Lean Problem Solving include: Identifying and solving problems in less time and achievement of measurable results. Involving everyone in the problem solving process.

lean problem solving process
Table 6.4.1: Steps in the Toyota Lean Problem-Solving Process; Step Action; Step 1: Clarify the problem. Step 2: Analyze the problem (genchi genbutsu is the Toyota practice of thoroughly understanding a condition by confirming information or data through personal observation at the source of the condition; the Japanese phrase essentially means "go and see"). 28

Problem Solving Methods Steps Process Examples Riset
Lean problem solving is a systematic approach to identifying and eliminating waste and inefficiencies in manufacturing processes. It involves applying various tools and techniques to.

Keep it Lean more productive and motivated The Techwriting Engineer
The Problem-Solving Process. The process of problem-solving is a methodical approach that involves several distinct stages. Each stage plays a crucial role in navigating from the initial recognition of a problem to its final resolution. Let's explore each of these stages in detail. Step 1: Identifying the Problem. This is the foundational.
A3 A Lean Approach to Problem Solving
What are the Four Lean Tools for Simple Problem Solving? 5G The most basic and first of four lean tools for simple problem solving is 5G. Also known as the 5 Gen Methodology or the 5 Gen principle, 5G is a popular Japanese problem-solving method used for improving various manufacturing activities.
Problem Solving Methods Lean Enterprise Academy
Type 2: Gap from Standard: structured problem-solving that focuses on defining the problem, setting goals, analyzing the root cause, and establishing countermeasures, checks, standards, and follow-up activities. The aim is to prevent the problem from recurring by eliminating its underlying causes.
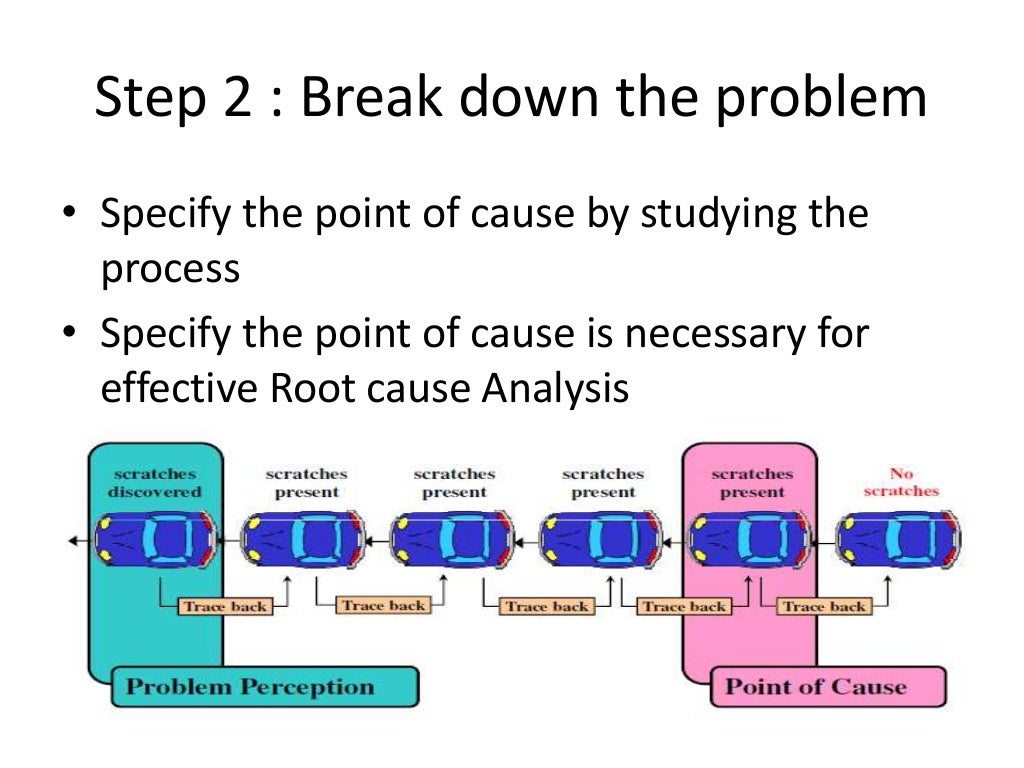
Problem Solving Techniques LEAN
A3 Problem solving is a structured and systematic approach to problem-solving that originated with the lean manufacturing methodology. It visualizes the problem-solving process using a one-page document known as an A3 report. The A3 report provides an overview of the problem, data analysis, root causes, solutions, and results in a clear and.
Lean Six Sigma Mind Map
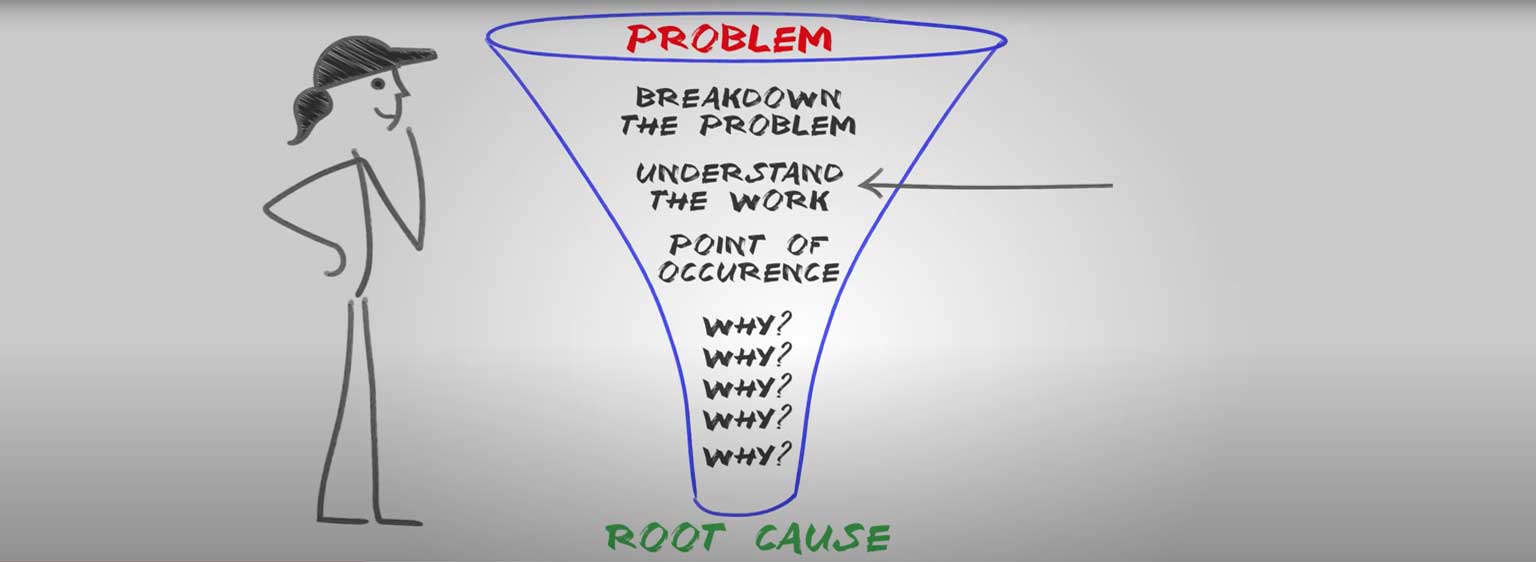
Updated onMarch 7, 2023. Root cause analysis (RCA) is a problem-solving methodology used to identify the underlying cause of a problem, incident, or adverse event. Simply put, it is pinpointing the root of the problem to solve and prevent it from happening again. When faced with a problem, we usually try to get to the bottom of it.
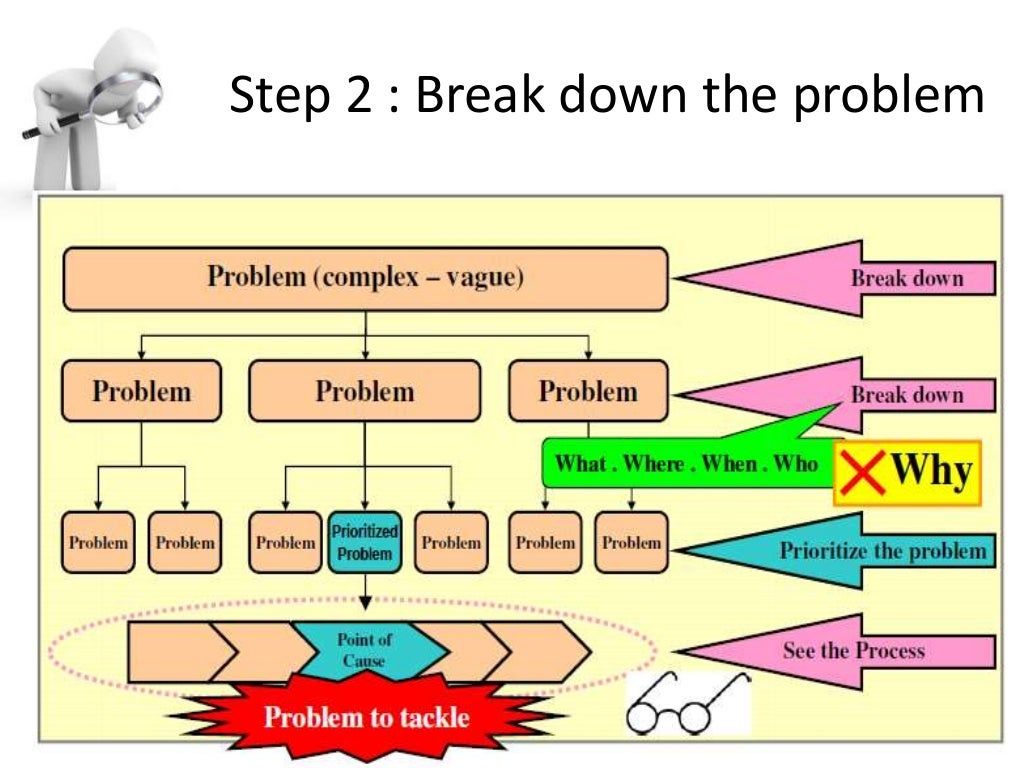
lean problem solving en que situaciones puede aplicarse
Ver1 Developing your Lean Journey The Lean Transformation Framework (LTF) helps determine the best lean journey for your situation. Based around five questions, it starts by asking "What problem are we trying to solve?" We use the LTF to help decide how to support your needs and progress your lean journey.
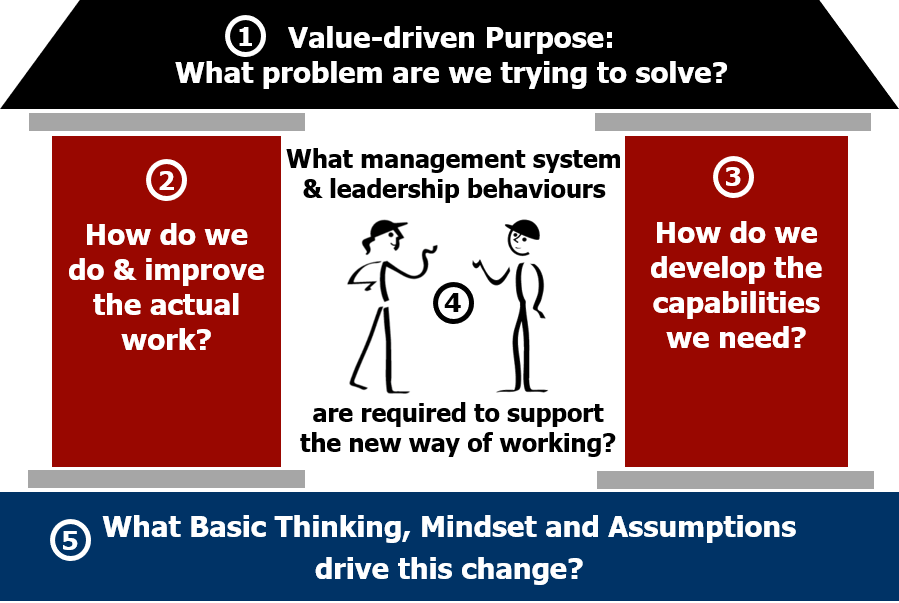
Purpose Rapid Problem Solving Lean Enterprise Academy
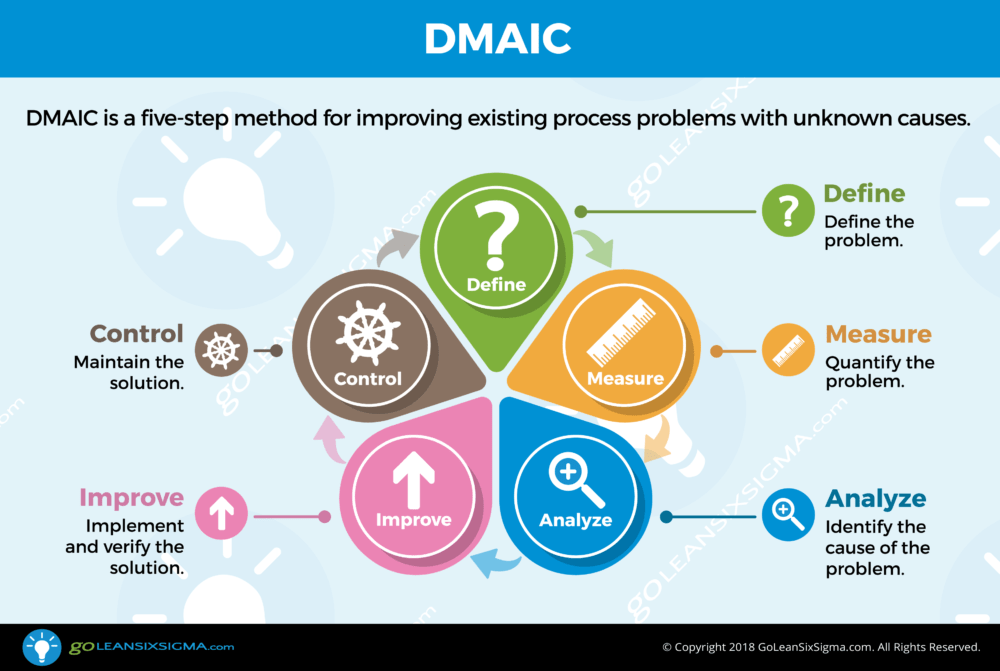
DMAIC is the problem-solving approach that drives Lean Six Sigma. It's a five-phase method—Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control—for improving existing process problems with unknown causes. DMAIC is based on the Scientific Method and it's pronounced "duh-may-ik."

what is the 3rd step in the 4 step problem solving process
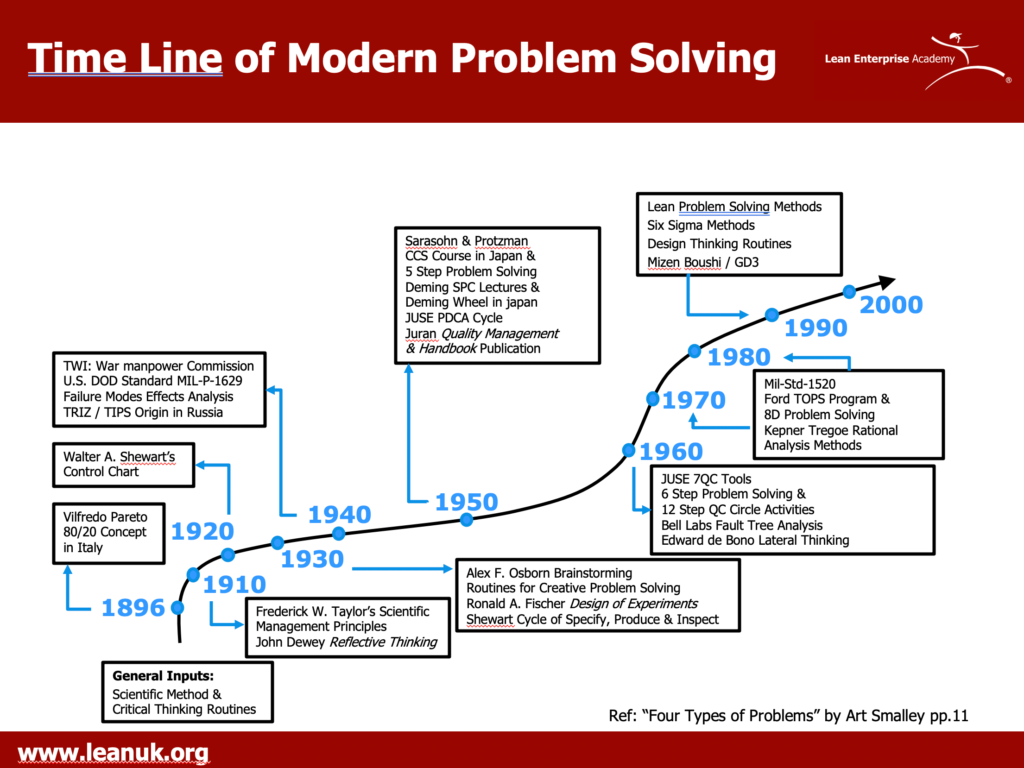
The four types described are 1) good troubleshooting routines, 2) gap from standard deviation situations, 3) target state improvement opportunities, and 4) more open-ended or innovation-based routines. There is some overlap between adjacent types, of course, but each has its own purpose and methods associated with it.
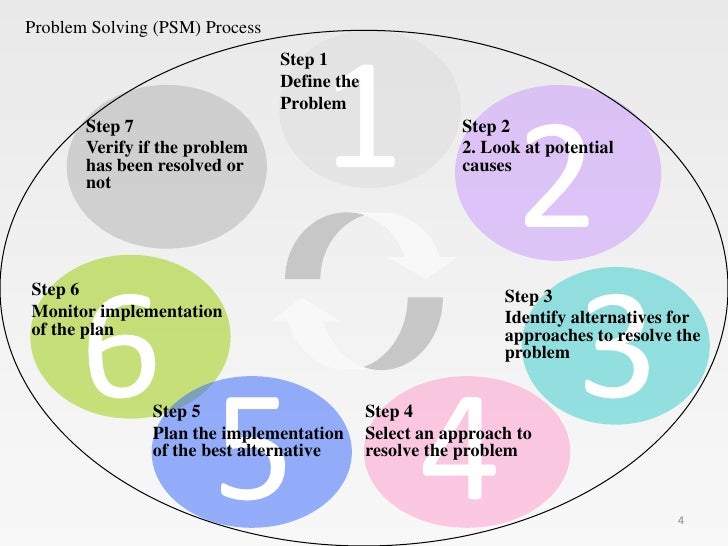
seven step problem solving model
A problem-solving methodology (or process): Most lean practitioners know "the A3" as a problem-solving process guided by specific steps or questions.
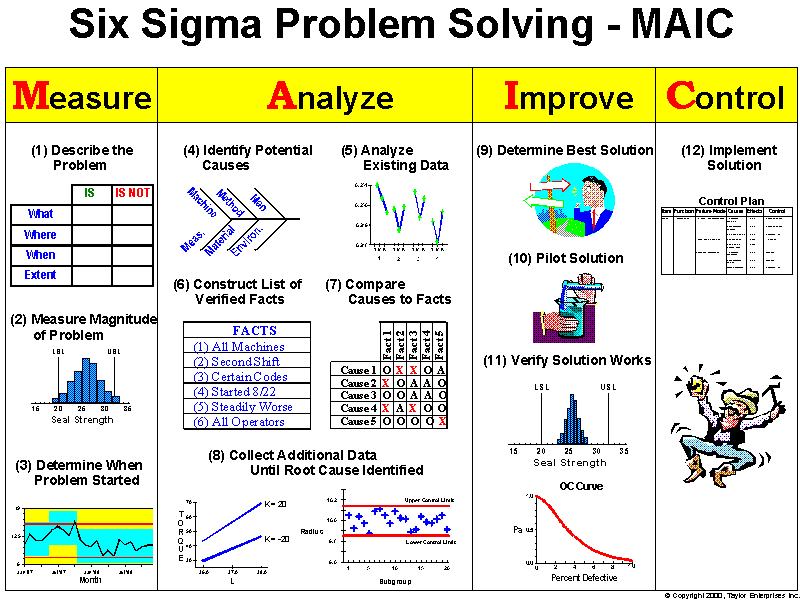
Six Sigma Problem Solving Process Taylor Enterprises
Problem Solving In a lean transformation or any process improvement effort, identifying and closing gaps between current and target conditions. In a lean management system, everyone is engaged in problem solving, guided by two key characteristics:
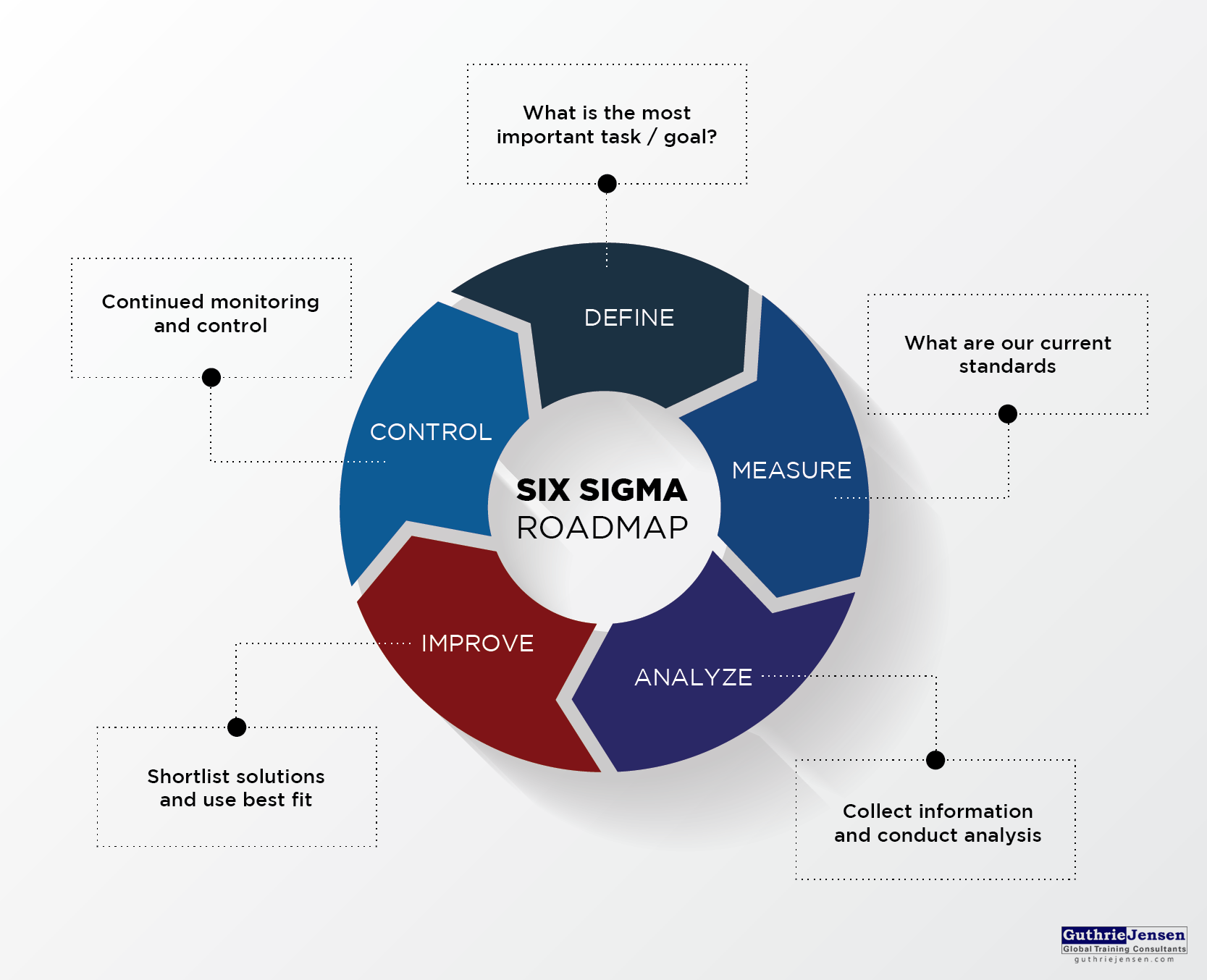
INSIGHTS The GuthrieJensen Blog Top Project Management Approaches Explained [A Visual Guide]
- Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve & Control - is the 5-Step model for Lean Six Sigma and there's a set of required tollgates at the end of each phase. These tollgates outline what has to be done in order to move the problem-solving process forward.